Researchers from Japan have developed a self-powered artificial synapse that distinguishes colors with high resolution across the visible spectrum, with a range of capability and level of accuracy that approaches those of the human eye. This technology could significantly benefit autonomous vehicles by enabling more accurate and efficient recognition of traffic lights, road signs and obstacles.
The device, which integrates dye-sensitized solar cells, generates its electricity and can perform complex logic operations without additional circuitry, enabling capable computer vision systems integrated in everyday devices.
Why does the industry need to see color?
As artificial intelligence and smart devices continue to evolve, machine vision is taking an increasingly pivotal role as a key enabler of modern technologies. Unfortunately, despite much progress, machine vision systems still face a major problem: processing the enormous amounts of visual data generated every second requires substantial power, storage and computational resources. This limitation makes it difficult to deploy visual recognition capabilities in edge devices such as autonomous vehicles.
Interestingly, the human visual system offers a compelling alternative model. Unlike conventional machine vision systems that have to capture and process every detail, our eyes and brain selectively filter information. Neuromorphic computing, which mimics the structure and function of biological neural systems, has thus emerged as a promising approach to overcome existing hurdles in computer vision. However, two major challenges have persisted. The first is achieving color recognition comparable to human vision, the second is eliminating the need for external power sources to minimize energy consumption.
The research
A research team led by associate professor Takashi Ikuno from the School of Advanced Engineering, Department of Electronic Systems Engineering, at the Tokyo University of Science (TUS) in Japan, has developed a solution. Their paper, published in Volume 15 of the journal Scientific Reports on May 12, 2025, introduces a self-powered artificial synapse capable of distinguishing colors with remarkable precision. The study was co-authored by Hiroaki Komatsu and Norika Hosoda, also from TUS.
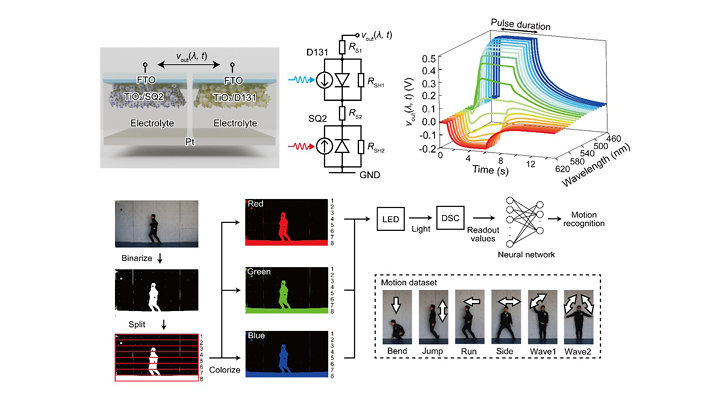
The researchers created a device by integrating two different dye-sensitized solar cells, which responded differently to various wavelengths of light. Unlike conventional optoelectronic artificial synapses that require external power sources, the proposed synapse generates its electricity via solar energy conversion. This self-powering capability makes it particularly suitable for edge computing applications, where energy efficiency is crucial.
The research found that the system can distinguish between colors with a resolution of 10nm across the visible spectrum — a level of discrimination approaching that of the human eye. Moreover, the device also exhibited bipolar responses, producing positive voltage under blue light and negative voltage under red light. This makes it possible to perform complex logic operations that would typically require multiple conventional devices.
“The results show great potential for the application of this next-generation optoelectronic device, which enables high-resolution color discrimination and logical operations simultaneously, to low-power artificial intelligence (AI) systems with visual recognition,” noted Dr Ikuno.
Real-world application
To demonstrate a real-world application, the team used their device in a physical reservoir computing framework to recognize different human movements recorded in red, green and blue. The system achieved an impressive 82% accuracy when classifying 18 different combinations of colors and movements using a single device, rather than the multiple photodiodes needed in conventional systems.
“We believe this technology will contribute to the realization of low-power machine vision systems with color discrimination capabilities close to those of the human eye, with applications in optical sensors for self-driving cars, low-power biometric sensors for medical use and portable recognition devices,” said Dr. Ikuno.
In related news, NXP Semiconductors has unveiled its third-generation S32R47 imaging radar processor in 16nm FinFET technology, delivering up to 2x processing performance in the radar MPU, in a 38% smaller IC footprint than its previous generation. It also includes AI/ML support for features like enhanced direction of arrival (DoA) processing and object classification. Click here to read the full story